42 atp diagram labeled
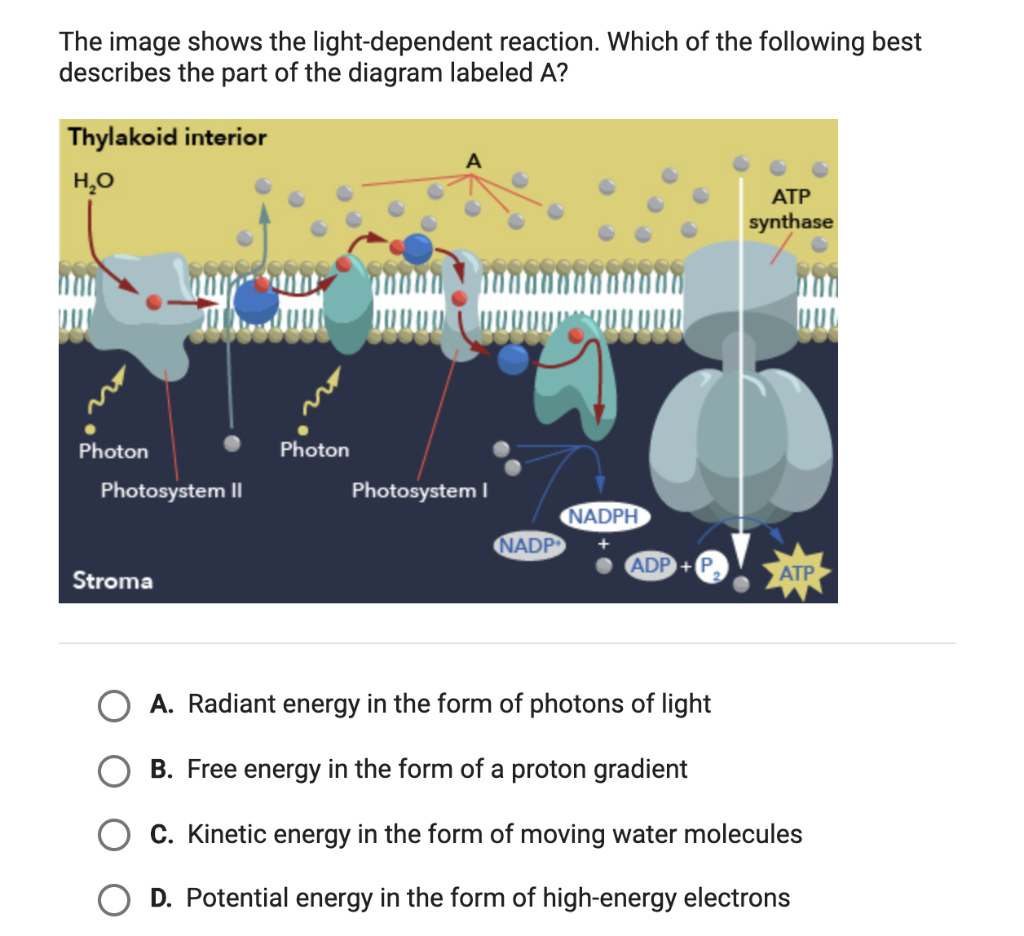
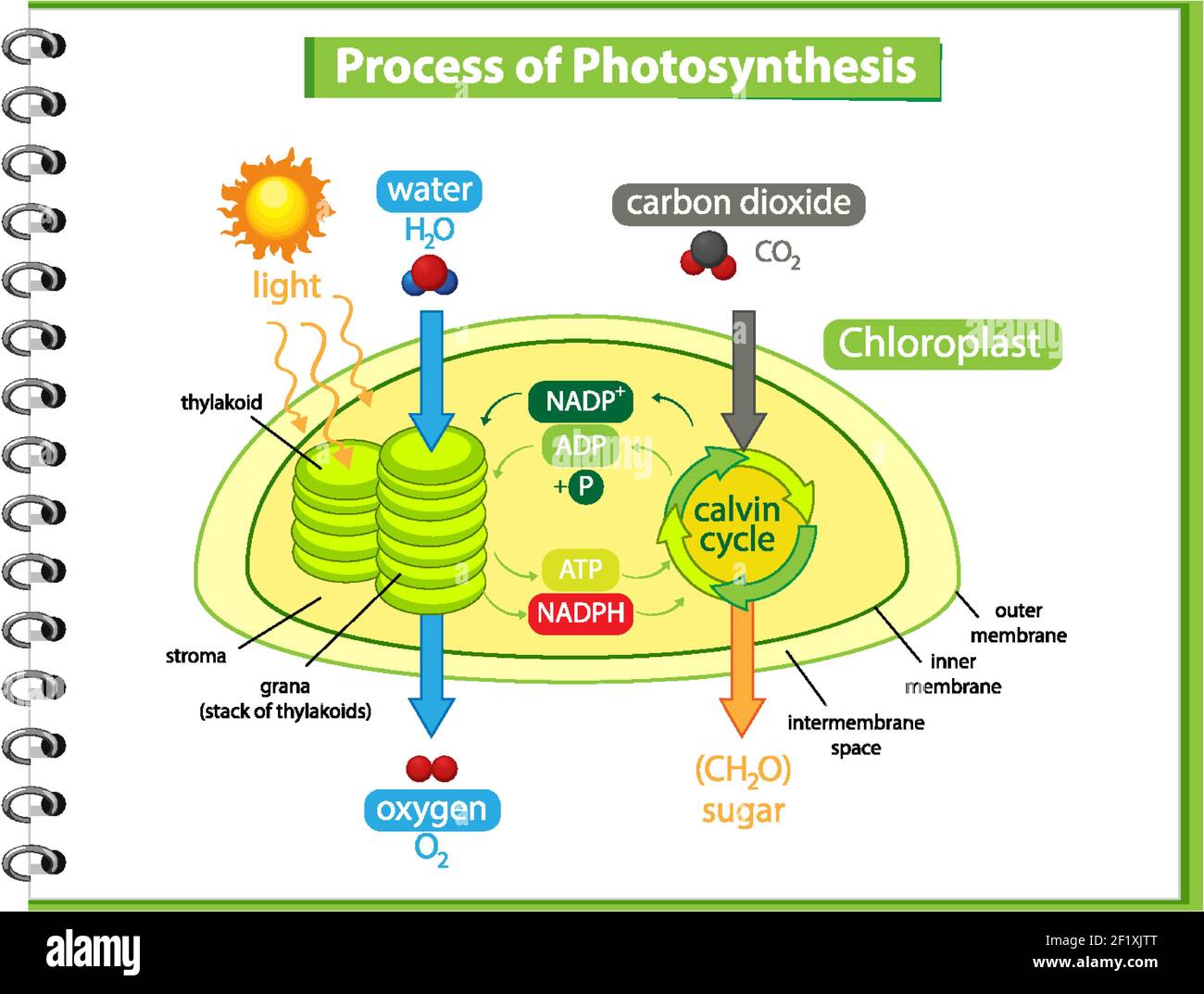
Thylakoid membrane in a cell - function, structure, and definition The thylakoid membrane diagram labeled above shows the structures found in the membrane. Membrane The membrane is the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, with photosynthetic pigments embedded directly in it. The membrane consists of an alternating pattern of dark and light bands, each measuring 1 nanometre. Photosynthesis Diagram - Explore the Secret of Nature - Edrawsoft Photosynthesis has two phases, they are commonly known as "Photosynthesis Light Reaction" and "Photosynthesis Dark Reaction". We will analyze these two phases one by one. 1. Photosynthesis Light Reaction: ADP + NADP + H2O → ATP +NADPH + H ion + O2 This reaction of photosynthesis only happens when light is available.
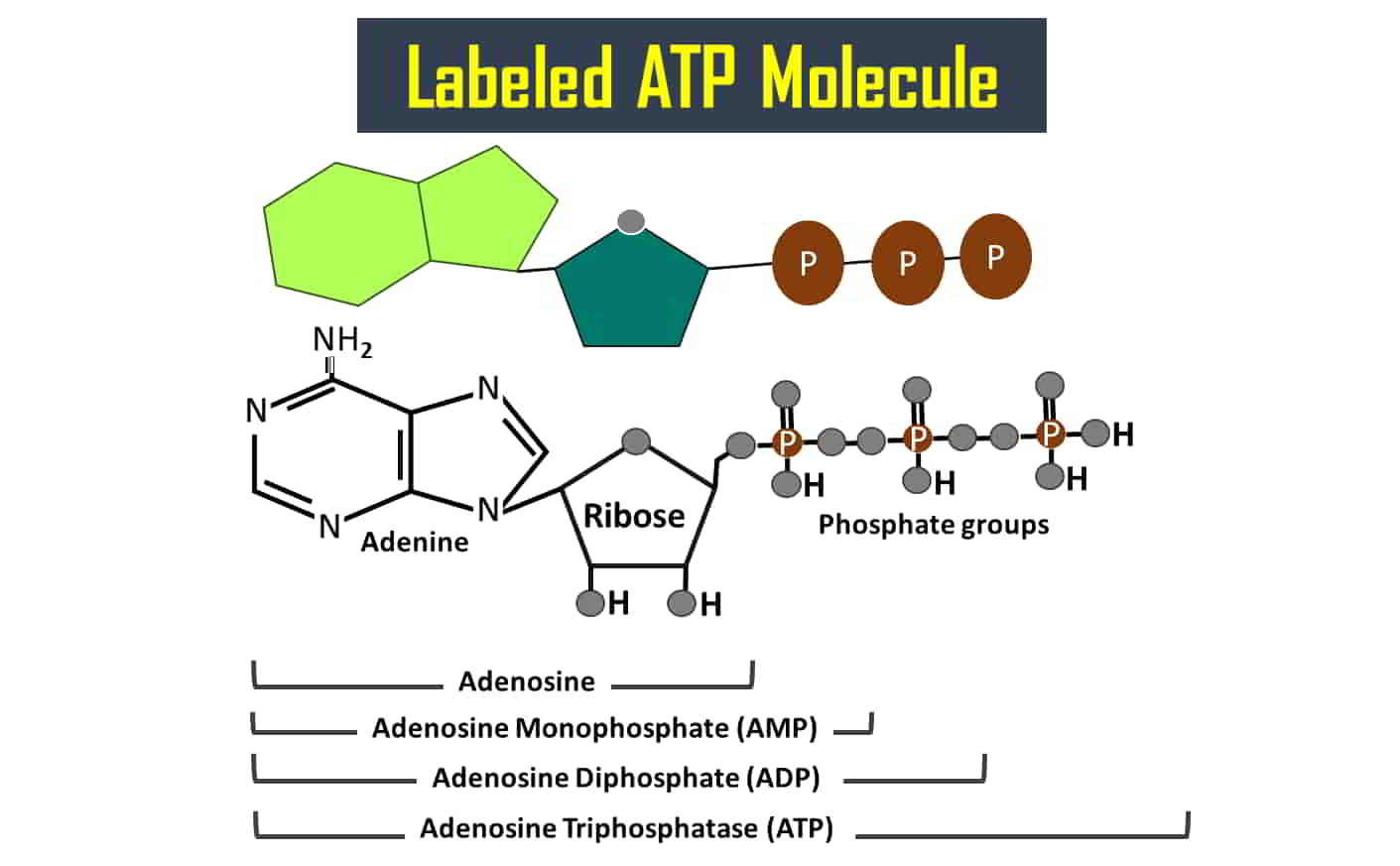
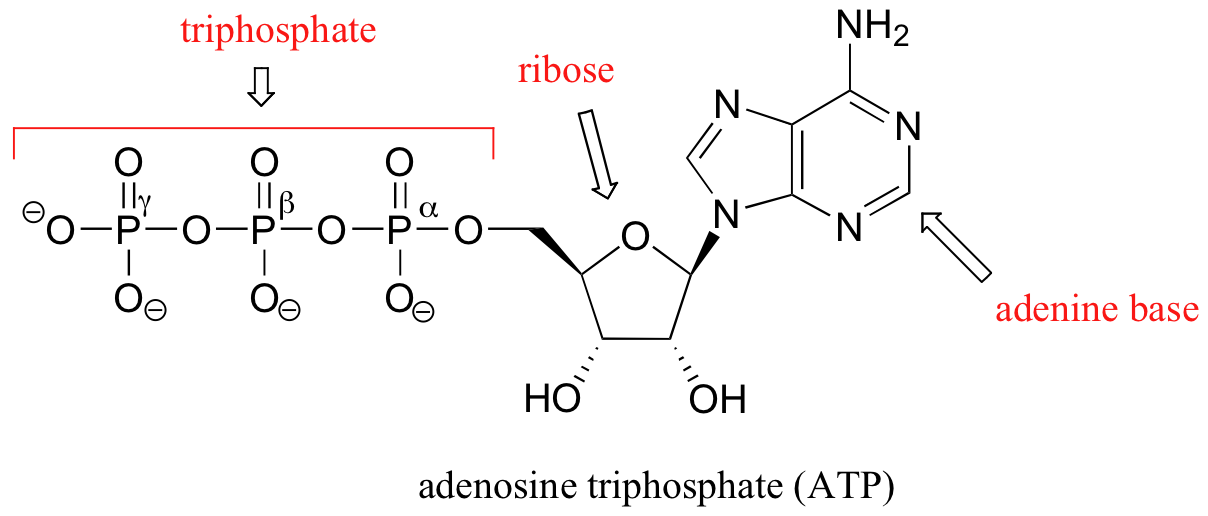
Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The body is a complex organism, and as such, it takes energy to maintain proper functioning. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups. ATP is commonly referred to as the "energy currency ...

Atp diagram labeled
What is ATP Synthase? Structure and Function - Study.com The mitochondrion, less often referred to as ATP mitochondria (plural), is an organelle (a specialized structure that performs a specific job within a cell) primarily responsible for energy... Animal Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure - Research Tweet During this, energy is derived and converted into ATP from fats, carbohydrates, and other biomolecules. Mitochondria almost act as independent cellular organelle and have their own DNA, know as mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) which is an exact replication of the mother's DNA. Plant Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure Mitosis- definition, purpose, stages, applications with diagram Mitosis definition. Mitosis is the process of cell division in which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells, resulting in cell duplication and reproduction. The number of chromosomes is preserved in both the daughter cells. Mitosis is a short period of chromosome condensation, segregation, and cytoplasmic division.
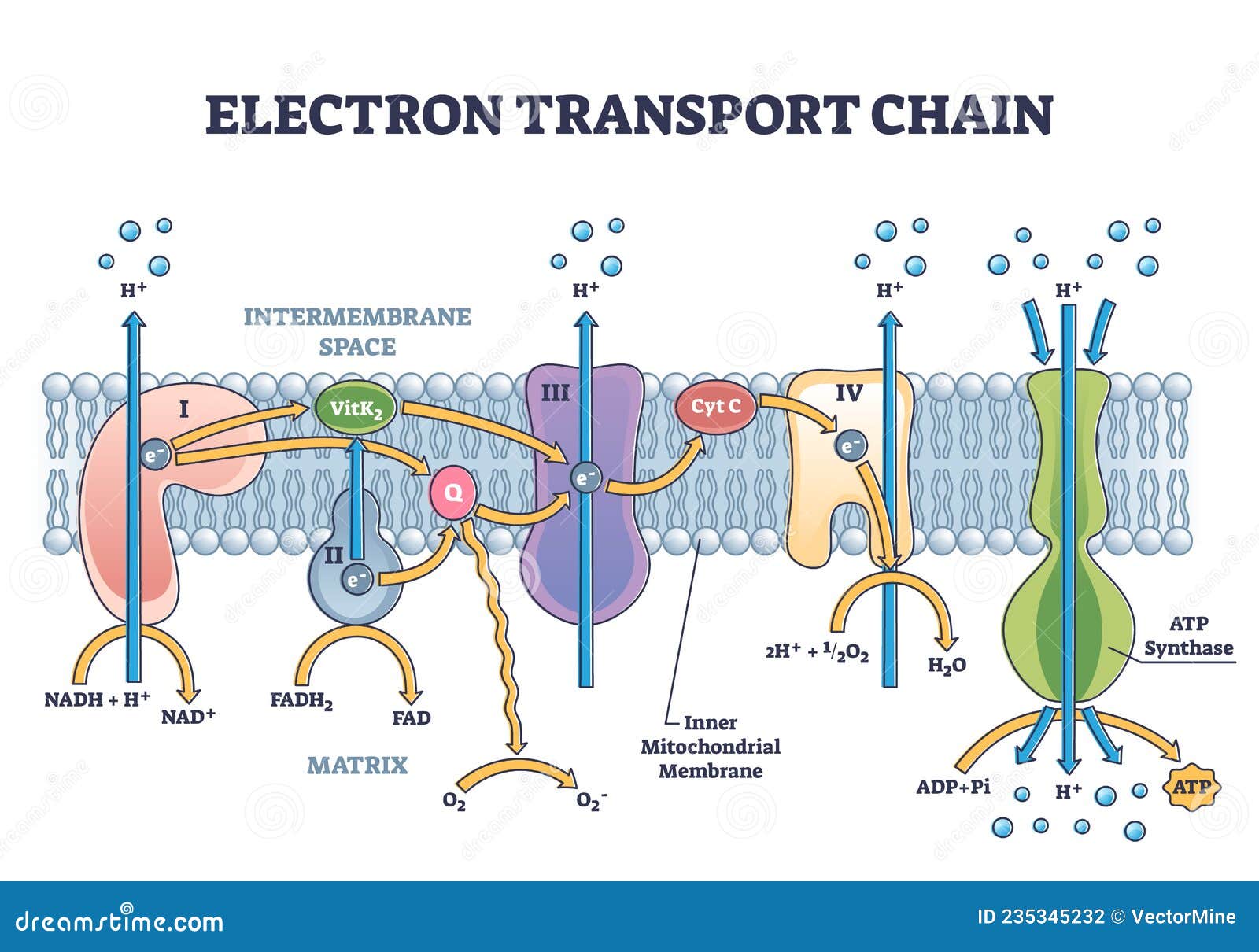
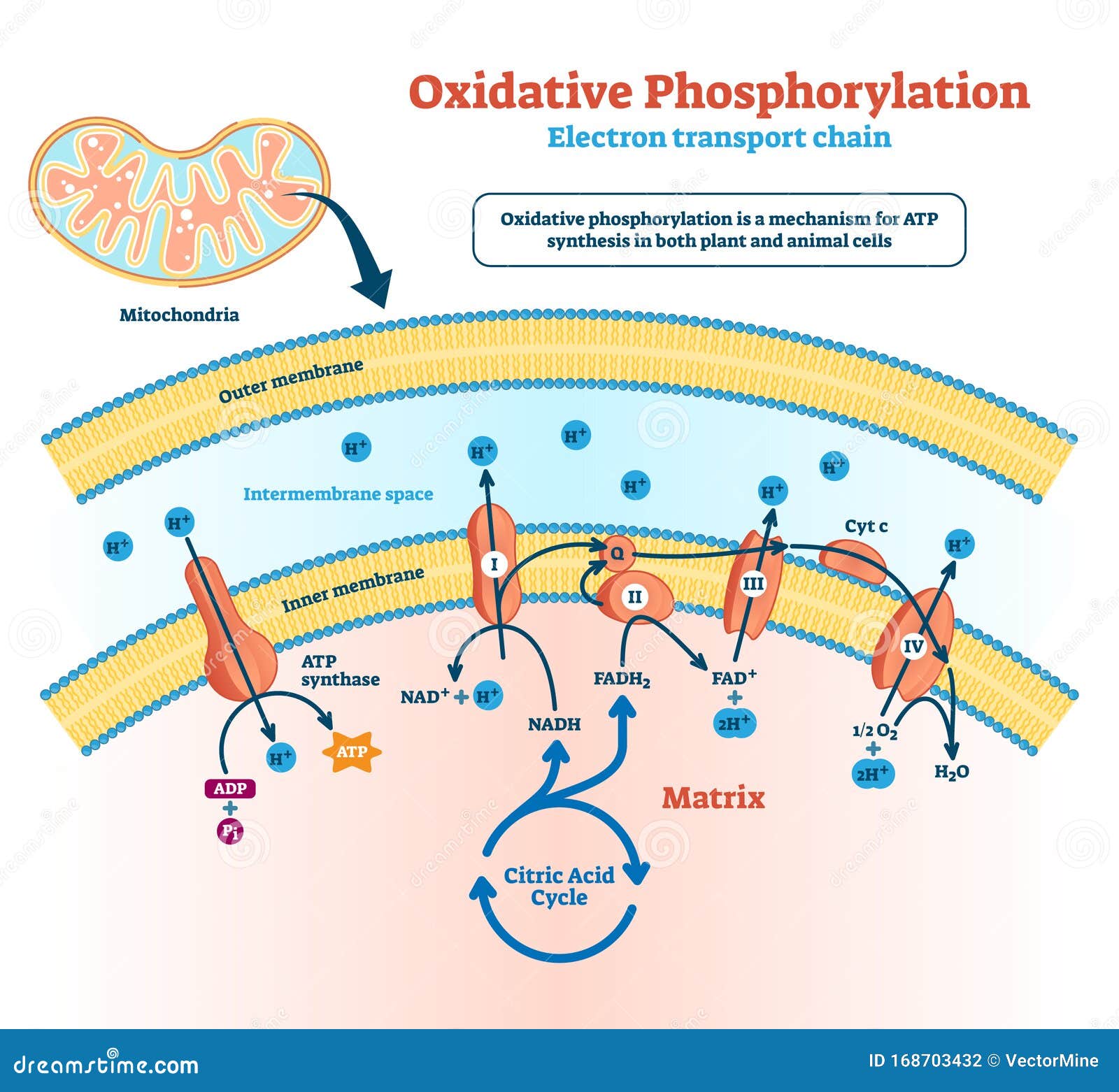
Atp diagram labeled. Biochemistry, Electron Transport Chain - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinone (CoQ), is made up of quinone and a hydrophobic tail. Its purpose is to function as an electron carrier and transfer electrons to complex III. Coenzyme Q undergoes reduction to semiquinone (partially reduced, radical form CoQH-) and ubiquinol (fully reduced CoQH2) through the Q cycle. Liver - Anatomy and Function of the Human Liver - Innerbody Liver. Weighing in at around 3 pounds, the liver is the body's second largest organ; only the skin is larger and heavier. The liver performs many essential functions related to digestion, metabolism, immunity, and the storage of nutrients within the body. These functions make the liver a vital organ without which the tissues of the body would ... Trey Cerney Plant Cellular Respiration Diagram Labeled : Chloroplast Vs Mitochondria Process Educational Scheme Vector Illustration Labeled Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Interaction Diagram Graphic With Green Plant Chemical Formula Or Atp Energy Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock - Jun 12, 2021 · diagrammatic illustration of the cellular respiration pathway (source: Tennis Court Explained | Diagram Labeled With Dimensions & Court Areas A tennis court can be of a variety of surfaces (explained below) each having different characteristics from the other. To understand a tennis court better, look at the tennis diagram below to have visual information. In the following diagram, different parts of the tennis court are labeled with dimensions. Diagram of Tennis Court
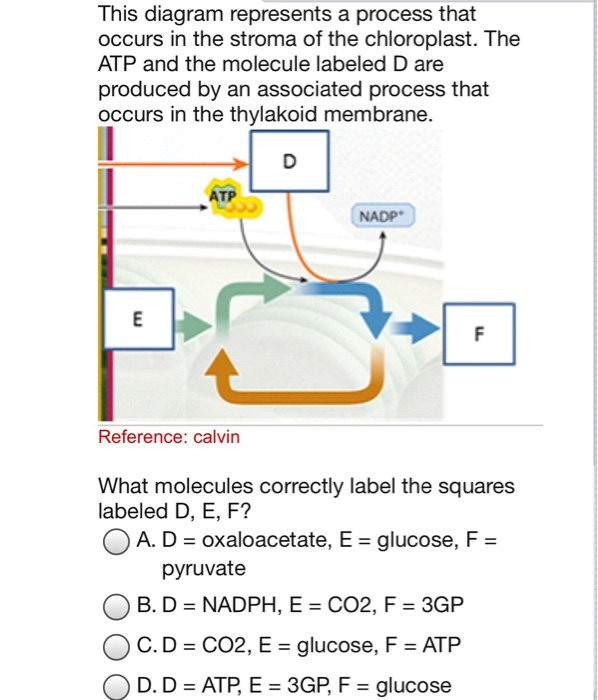
› metabolismMetabolism of Carbohydrates: 10 Cycles (With Diagram) Thus, light is responsible for the flow of electrons from H 2 O to NADPH with a concomitant generation of ATP. The Calvin cycle: The dark phase of photosynthesis is referred to as Calvin cycle. In this cycle, the ATP and NADPH produced in the light reaction (described above) are utilized to convert CO 2 to hexoses and other organic compounds ... Marcelino Fischels - Blogger Animal Cell Diagram Labeled Gcse - Cell structure teaching resources - the science teacher : For tutoring please call 856.777.0840 i am a recently retired registered nurse who helps nursing students pass their nclex. ... cell labels / The diagram, like the one above, will include labels cellular respiration converts oxygen and sugar into atp ... › questions-and-answers › q8Answered: Q8. (1) Complete the following genetic… | bartleby (1) Complete the following genetic diagram to show how parents who did not suffer from haemophilia, could have a son wit h haemophilia but also other children who did not suffer from haemophilia. Phenotype of parents Genotype of parents Genotype of gametes Normal male Normal female Genotype of offspring Phenotype of offspring (1) What is the ... Chloroplast: Meaning, Structure, Analogy - Embibe Fig: A Labeled Diagram of Chloroplast. Chloroplast Structure ... NADPH 2 and ATP are the assimilatory powers of photosynthesis. Transfer of \( {\text{C}} { {\text{O}}_ {\text{2}}}\) obtained from the air to \(5\) carbon sugar in the stream during the dark reaction. 10. The chloroplasts with the nucleus and cell membrane and ER are the key ...
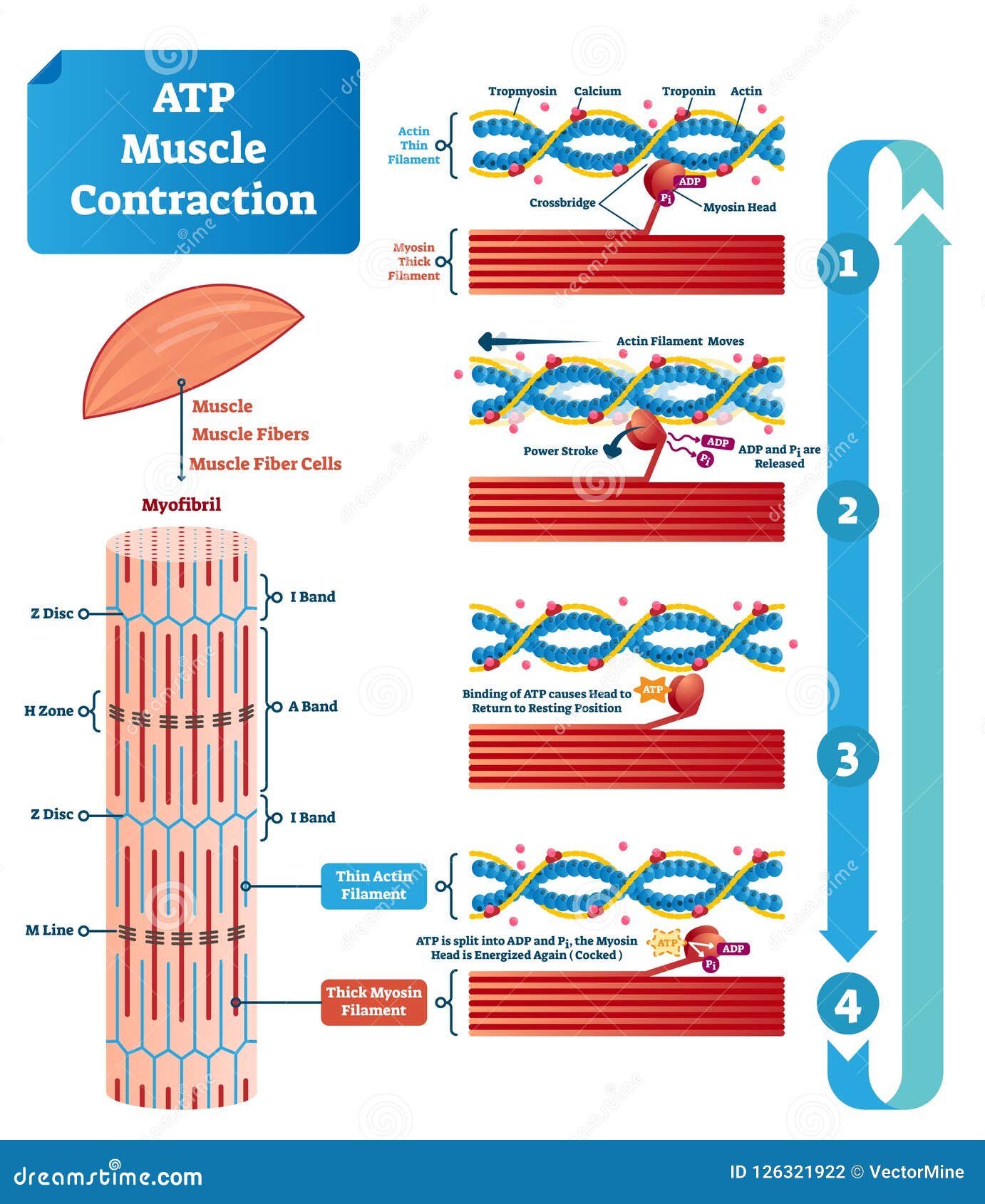
Lacrimal apparatus: Anatomy, parts & function | Kenhub Bulbar conjunctiva (cranial view) Anatomy and parts Lacrimal gland. This gland is about the size of an almond, and sits within the lacrimal fossa, located in the superior and outer edge of the orbital roof.The gland is divided into two sections anatomically. These are the small palpebral portion that lies closer to the eye, and the orbital portion that forms around four ducts. Cell Organelles- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram The oxidation of various substrates in the cell to release energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is the primary purpose of mitochondria. ... Labeled Diagram; Animal Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram; Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes- Definition, 47 Differences, Structure, Examples; Amazing 27 Things Under The ... Muscle Contraction & Sliding Filament Theory - TeachPE.com The diagram above shows a partially contracted muscle where there is more overlapping of the myosin and actin with lots of potential for cross bridges to form. The I - bands and H - zone is shortened. Fully Contracted Muscle The diagram above shows a fully contracted muscle with lots of overlap between the actin and myosin. How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ATP is made up of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate molecules. ATP contains one adenine (blue), one sugar (pink), and three phosphate groups. ATP Meaning ATP follows the same rules of...
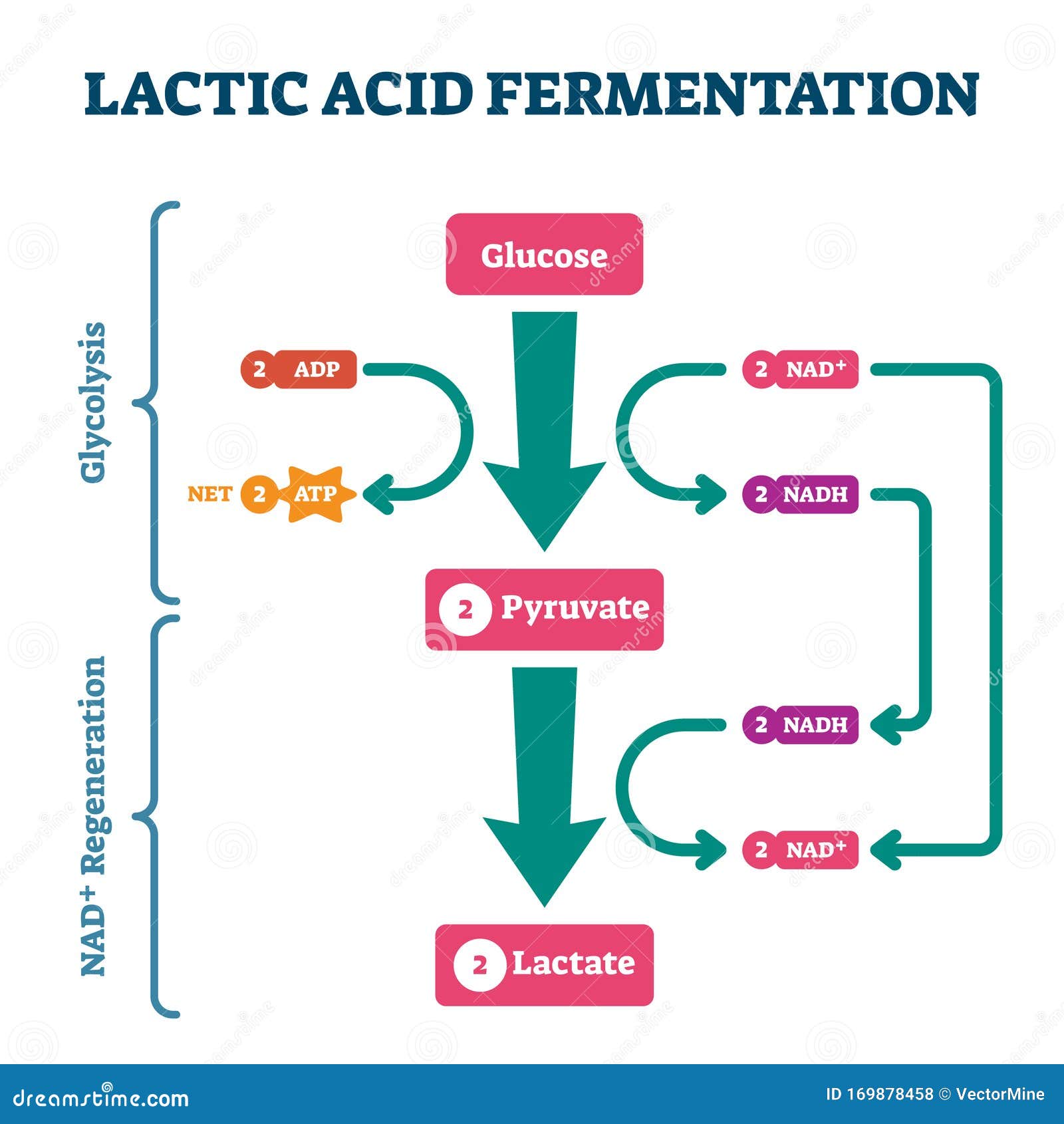
Glycolysis Explained in 10 Easy Steps (With Diagrams) Phosphofructokinase, with magnesium as a cofactor, changes fructose 6-phosphate into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Details: In the third step of glycolysis, fructose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose- 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP).Similar to the reaction that occurs in step 1 of glycolysis, a second molecule of ATP provides the phosphate group that is added on to the F6P molecule.
Microsoft 365 productivity illustrations | Microsoft Docs Microsoft 365 information protection and compliance capabilities. Microsoft 365 includes a broad set of information protection and compliance capabilities. Together with Microsoft's productivity tools, these capabilities are designed to help organizations collaborate in real time while adhering to stringent regulatory compliance frameworks.
Action potential - Definition, Steps, Phases | Kenhub An action potential is defined as a sudden, fast, transitory, and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential; that property is called the excitability. This article will discuss the definition, steps and phases of the action potential. Contents Definition Steps
Cellular Respiration- Definition, Equations, Types, Steps, Products Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is an inorganic compound that acts as an energy-carrying molecule by capturing energy produced from chemical reactions. ATP is a nucleotide molecule consisting of three main structural units; nitrogenous base, adenine, sugar unit, ribose, and three phosphate groups bound to the ribose backbone.
FAA Airport Diagrams - Federal Aviation Administration FAA Airport Diagrams. FAA. Airport Diagrams. The fields below compose a list of search parameters for searching the FAA Diagrams site. Please enter your search criteria and then click on Search. FAA Diagram Search. Airport identifier: (Example: KOKC or OKC) State:
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ATP_synthaseATP synthase - Wikipedia ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage ... Subunits of the enzyme are labeled accordingly. ... in the adjacent diagram, this is ...
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38ATP ( Glucose + 6 Oxygen → 6 Carbon Dioxide + 6 Water + ATP ) * Value is not constant for all aerobic organisms. May range from 34 to 38 net ATP.
Understanding the Azure Information Protection unified labeling scanner ... 2. Inspect and label files. 3. Label files that can't be inspected. For more information, see Files not labeled by the scanner. 1. Determine whether files are included or excluded for scanning. The scanner automatically skips files that are excluded from classification and protection, such as executable files and system files.
Label Atp Molecule - the atp molecule chemical and physical properties ... Label Atp Molecule - 16 images - 35 label each part of the atp molecule labels database 2020, photosynthesis light reactions, energy atp and adp sciencemusicvideos, simple diagram atp molecule diagramaica,
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Citric_acid_cycleCitric acid cycle - Wikipedia The above reactions are balanced if P i represents the H 2 PO 4 − ion, ADP and GDP the ADP 2− and GDP 2− ions, respectively, and ATP and GTP the ATP 3− and GTP 3− ions, respectively. The total number of ATP molecules obtained after complete oxidation of one glucose in glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation is ...
microbenotes.com › krebs-cycleKrebs cycle / Citric acid cycle / TCA Cycle with steps and ... Mar 10, 2022 · Image Source: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. The oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate forms a link between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. In this process, the pyruvate derived from glycolysis is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl CoA and CO 2 catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in the mitochondrial matrix in eukaryotes and in the cytoplasm of the prokaryotes.
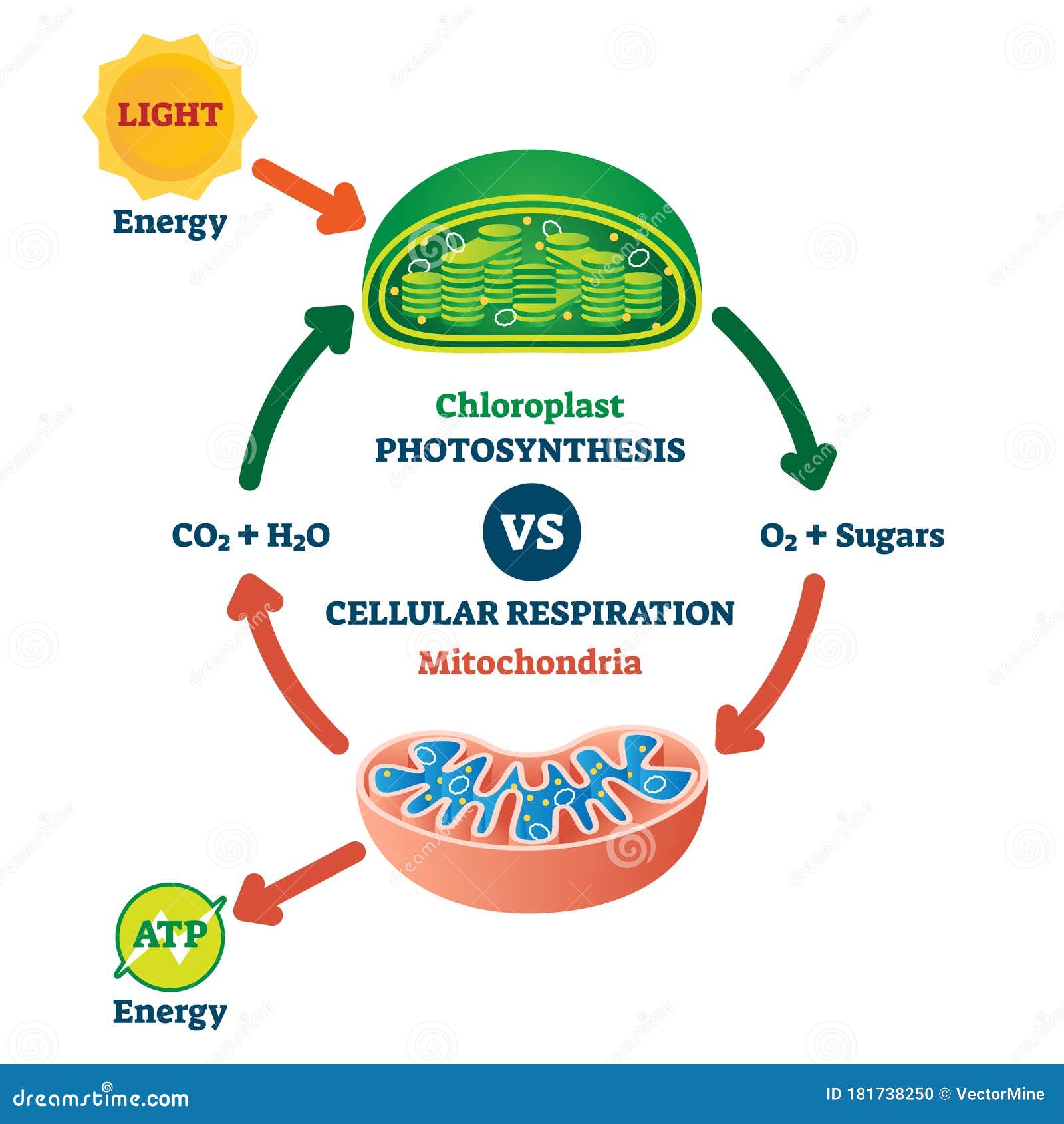
Difference Between Mitochondria and Chloroplast: Parts, Diagrams Mitochondria is found both in animal and in plant cells, whereas chloroplast is found only in plant cells. Mitochondria are responsible for generating energy for the cell in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). On the other hand, chloroplasts perform Photosynthesis in a plant cell. Also Read:- Vegetative Propagation in Plants.
The TCA Cycle - Steps - Krebs Cycle - TeachMePhysiology In order for ATP to be produced through oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are required for ATP to pass down the electron transport chain. These electrons come from electron carriers such as NADH and FADH₂, which are produced by the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA cycle, also known as the Kreb's/Citric Acid cycle). In this article we will outline the steps and regulation of this essential ...
How To Become A Tennis Umpire? Exclusive Guide + Inside Tips To become a tennis umpire, you go through different courses and training programs. After that, you have to pass the one-day line umpire course to get familiar with the responsibility of the line umpire. Aside from this, you must have sharp eyesight, be very quick at your reactions, and be calm in your mind. 2.
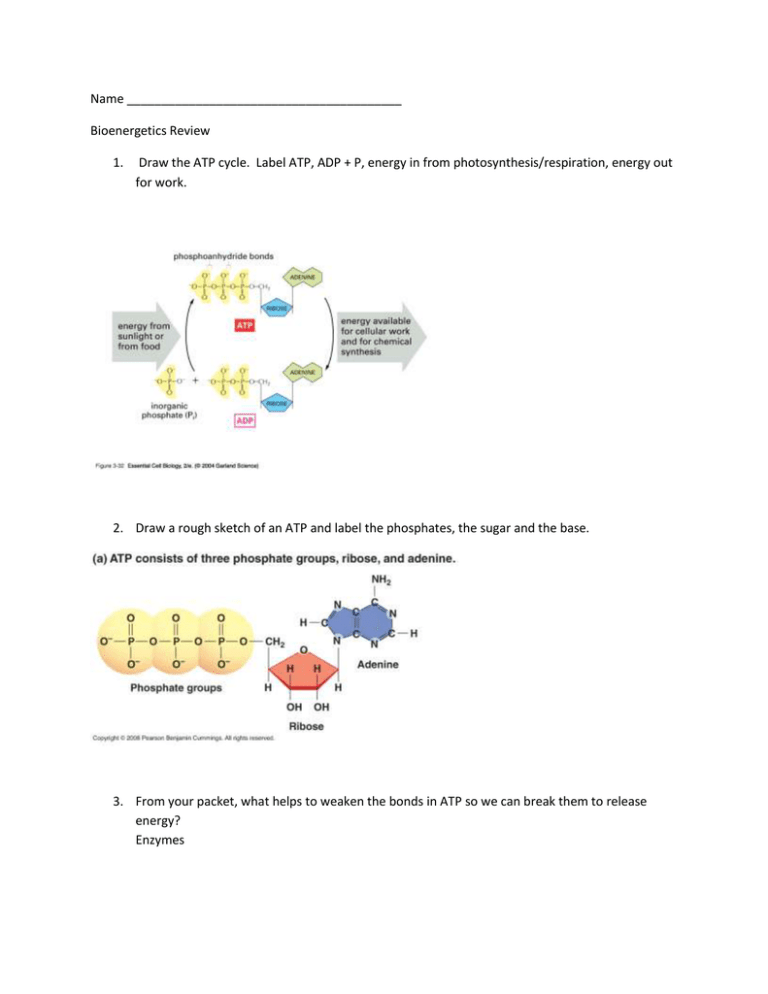
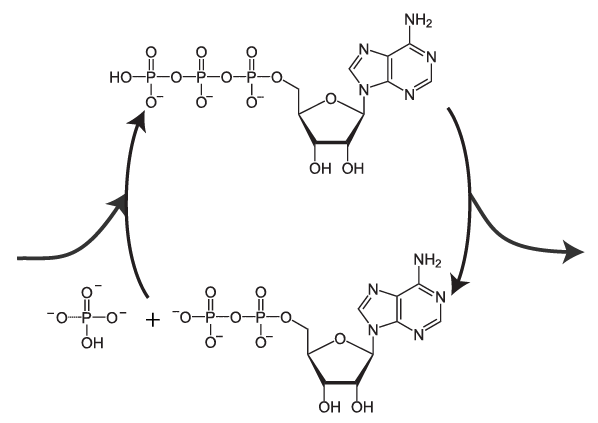
ATP and ADP: Definition, Formation, Examples I ResearchTweet ATP to ADP Energy Release. As the ATP molecule consist of 3phosphate molecule and an adenine molecule, thus when ATP is converted to ADP, a phosphate molecule is lost in this process. The reaction can be written as ATP → ADP + P i. Thus, this reaction results in energy released which is used by the cells to perform the biological process.
Cy3-ATP labeling of unfixed, permeabilized mouse hair cells - Nature Cy3-ATP labels the tips of cochlear stereocilia. (a) IHCs labeled with Cy3-ATP at P3.5.Z-projections using maximum intensity. Increasing the image gain (right) shows that shorter stereocilia also ...
microbenotes.com › plant-cellPlant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled ... Feb 16, 2022 · Figure: Labeled diagram of plant cell, created with biorender.com. The typical characteristics that define the plant cell include cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin, plastids which play a major role in photosynthesis and storage of starch, large vacuoles responsible for regulating the cell turgor pressure.
› dna › recombinant-dnaRecombinant DNA Technology (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion They require Mg++ ions and ATP for their functioning. Such types of restriction endonucleases cleave the DNA about 1000 bp away from the 5′ end of the sequence ‘TCA’ located within the recognition site. Important examples of Type-I restriction endonuclease enzyme are EcoK, EcoB, etc. Type-II Restriction Endonucleases:
Mitosis- definition, purpose, stages, applications with diagram Mitosis definition. Mitosis is the process of cell division in which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells, resulting in cell duplication and reproduction. The number of chromosomes is preserved in both the daughter cells. Mitosis is a short period of chromosome condensation, segregation, and cytoplasmic division.
Animal Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure - Research Tweet During this, energy is derived and converted into ATP from fats, carbohydrates, and other biomolecules. Mitochondria almost act as independent cellular organelle and have their own DNA, know as mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) which is an exact replication of the mother's DNA. Plant Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure
What is ATP Synthase? Structure and Function - Study.com The mitochondrion, less often referred to as ATP mitochondria (plural), is an organelle (a specialized structure that performs a specific job within a cell) primarily responsible for energy...



























Post a Comment for "42 atp diagram labeled"