45 label the internal features of stomach and duodenum using the hints if provided.
Digestive lab Flashcards | Quizlet Label the mucous membrane tissue from the stomach using the hints if provided. Label the digestive abdominal contents using the hints if provided. Place the appropriate words and descriptions with the picture with the correct highlighted digestive accessory organ. Label the structures of the posterior thoracic wall using the hints if provided. Module 3 Study Guide ch 24 ch 25Catrina Greene BIO-169 ... - Course Hero Label the parts of the liver and gallbladder using the hints provided. Label the abdominal contents using the hints provided. Label the sagittal section of the mesenteries. Label the mucous membrane tissue from the stomach using the hints if provided. Correctly organize the events of the defecation reflex.
A&P 2 Lab Practical Final Flashcards - Quizlet Put the following structures of the lower respiratory tract in order from proximal to distal. Label these structures of the upper respiratory system. Label the anterior view of the larynx based on the hints if provided. Place the following words in order to show the pathway oxygen will diffuse across the respiratory membrane

Label the internal features of stomach and duodenum using the hints if provided.
Chambers of the Heart - Atria - Ventricles - TeachMeAnatomy 3 Clinical Relevance: Tetralogy of Fallot. The heart consists of four chambers: the two atria and the two ventricles. Blood returning to the heart enters the atria, and is then pumped into the ventricles. From the left ventricle, blood passes into the aorta and enters the systemic circulation. From the right, it enters the pulmonary circulation ... The Dogfish Shark—Structure and FUNction! - Carolina.com The stomach's longitudinal folds, called rugae, allow the stomach to expand. Discuss these digestive structures in light of the fact that the shark does not chew its food but instead bites off and swallows large chunks of it. At a J-shaped turn along the digestive tube, the stomach leads into the duodenum. 23.1 Overview of the Digestive System - Anatomy & Physiology Muscularis mucosa —This thin layer of smooth muscle is in a constant state of tension, pulling the mucosa of the stomach and small intestine into undulating folds. These folds dramatically increase the surface area available for digestion and absorption. As its name implies, the submucosa lies immediately beneath the mucosa.
Label the internal features of stomach and duodenum using the hints if provided.. Medical Definitions - IFFGD Colonoscopy is a fiberoptic (endoscopic) procedure in which a thin, flexible, lighted viewing tube (a colonoscope) is threaded up through the rectum for the purpose of inspecting the entire colon and rectum and, if there is an abnormality, taking a tissue sample of it (biopsy) for examination under a microscope, or removing it. Colostomy quizlet.com › 338836225 › ap-ch-17-digestiveA&P Ch 17 Digestive Homework Flashcards - Quizlet Layers of alimentary canal wall Complete the following sentences that describe the alimentary canal and its walls. Then place the sentences in order, listing structures/layers from deep to superficial, starting with the small intestinal lumen. 9789386663542 Maple G05 Evs I (Science) Workbook Term 1 The Maple EVS - I (Science) textbooks and workbooks offer the following features: Interactive content that engages students through a range of open- ended questions that build curiosity and initiate exploration Opportunities for experimentation, analysis and synthesis of ideas and concepts Exposure to locally relevant environmental problem ... Pancreas histology: Exocrine & endocrine parts, function - Kenhub The pancreas is a large, mixed gland composed of five parts: the head, uncinate process, neck, body and tail. The location of the pancreas is mostly retroperitoneal, except for the tail. This organ extends from the C-shaped curve of the duodenum, passes behind the stomach and finishes at the hilum of the spleen.
23.3 The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus - Anatomy & Physiology In this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. The Mouth The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). Digestive system - Histology The digestive tract (a.k.a alimentary tract ), starts in the oral cavity and continues through the pharynx, to the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and terminates in the anal canal. Food moves along the digestive tract by peristalsis, the rhythmic contractions of the smooth muscle within the walls of the tube. Digestive lab Flashcards | Quizlet Label the mucous membrane tissue from the stomach using the hints if provided. Label the digestive abdominal contents using the hints if provided. Place the appropriate words and descriptions with the picture with the correct highlighted digestive accessory organ. Label the structures of the posterior thoracic wall using the hints if provided. › de › jobsFind Jobs in Germany: Job Search - Expat Guide to Germany ... Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language.
007460.pdf - LESSON 5 THE HUMAN BODY In the fifth lesson ... - Course Hero Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination are the four phases of digestion. Iningestion, you literally put the food into your digestive system when it enters your mouth. Indigestion, food is broken down mechanically by chewing and chemically by juices that target the breakdown of certain substances. GI Post Lab Flashcards | Quizlet Label the internal features of stomach and duodenum using the hints if provided. Label the histologic features of the duodenum using the hints if provided. Label the light micrograph of the colon using the hints provided. Label the light micrograph of the liver using the hints provided. 25.1 Internal and External Anatomy of the Kidney On the superior aspect of each kidney is an adrenal gland. Each kidney looks like the kidney bean and the renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the convex indentation of the kidney. Figure 25.1.2 Left Kidney. Internal Anatomy Lab 9 Digestive and resp Flashcards - Quizlet stomach Label the various abdominal structures using the hints provided. diaphragm liver pancreas transverse mesocolon duodenum transverse colon jejunum and ileum Label the various abdominal structures using the hints provided. anal canal rectum partial peritoneum greater omentum stomach visceral peritoneum
What Is Mitochondria (Structure, Diagram & Function) - BYJUS The mitochondrion is a double-membraned, rod-shaped structure found in both plant and animal cell. Its size ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometre in diameter. The structure comprises an outer membrane, an inner membrane, and a gel-like material called the matrix. The outer membrane and the inner membrane are made of proteins and phospholipid layers ...
23.1 Overview of the Digestive System - Anatomy & Physiology Muscularis mucosa —This thin layer of smooth muscle is in a constant state of tension, pulling the mucosa of the stomach and small intestine into undulating folds. These folds dramatically increase the surface area available for digestion and absorption. As its name implies, the submucosa lies immediately beneath the mucosa.
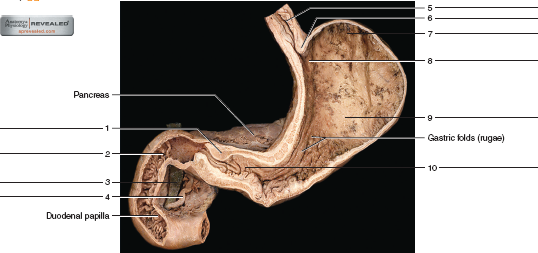
Post a Comment for "45 label the internal features of stomach and duodenum using the hints if provided."